Cost and Efficiency Benefits of Drones in Transmission & Distribution
There have been vast improvements in the processes and the technologies used in drone aerial intelligence gathering over the past decade. This technological and procedural leap is particularly evident when looking at the integration of drones into the T&D sector.
Here’s why:
- Reduced Manual Surveillance: Traditionally, inspecting transmission lines, towers, and other infrastructure required manual labor, often involving field technicians using ground-based equipment or even helicopters. These methods are time-consuming and might only capture some potential issues. Drones, however, can cover vast areas quickly and provide a high-resolution 360-degree view, allowing for a more thorough inspection.
- High-Quality Data Collection: Drones have state-of-the-art cameras and sensors that capture high-resolution images and data to pinpoint defects, corrosion, or vegetation encroachments that the human eye might miss.
- Quick Decision Making from Anywhere: Instead of waiting for ground teams to survey areas, analyze data, and make decisions, drones can stream rapid real-time data to remote command centers to aid in swift decision-making and promptly address problems wherever you are.
- Reduced Operational Costs: Deploying drones is considerably cheaper than using helicopters or large ground teams. There’s no need for fuel (in the case of helicopters), and fewer personnel are required on-site.
- Predictive Maintenance: Drones, combined with advanced data analytics, can predict when a component might fail or require maintenance. This predictive approach reduces unplanned downtime and saves costs associated with emergency repairs.
Our national footprint in the commercial T&D sector has revealed startling insights.
An astounding 95% of the poles we’ve inspected exhibited deficiencies. Even more concerning, some poles harbored up to 15 distinct issues and/or anomalies.
Safety First
With their ability to remotely conduct detailed inspections, drones eliminate the need for humans to be physically present in potentially dangerous zones. By harnessing the power of drones, inspections become more efficient and reduce the risk factor, ensuring a safer inspection landscape for all involved.
Examples include:
- Minimizing Human Risk: Manual inspections, especially in challenging terrains or at great heights, are fraught with dangers. Drones can navigate these areas without risking human lives.
- Anti-Collision Systems: Advanced drones are integrated with sensors that allow them to detect and avoid obstacles, ensuring safe navigation around complex T&D assets.
- Accurate Data Reduces Accidents: Precise data from drones ensures that maintenance crews know precisely where the problem is, ensuring they have the right tools and equipment for repairs and reducing the time they spend exposed to potential hazards.
- Remote Monitoring: Drones can be operated from a safe distance, ensuring that operators are not exposed to electrical fields, high-voltage equipment, or other dangers associated with T&D sites.
What Is the Value of Outsourced Data Analysis and Asset Management?
Data isn’t just king in the fast-evolving world of T&D drone inspections; it’s an ever-expanding empire. With their intricate data-capturing capabilities, drones generate terabytes of data. How do professionals transform this flood of information into actionable insights without getting overwhelmed or bogged down? Here’s where cutting-edge cloud-based data analytics portals, like ConnexiCore Cloud, have become a game changer. As a premier web-based data analytics portal, ConnexiCore Cloud eliminates the daunting task of manually sifting through terabytes of data—a process traditionally riddled with human error and inefficiencies. Instead, by leveraging outsourced data analysis and asset management through ConnexiCore Cloud, T&D companies not only harness specialized expertise and innovative tools but also unveil deeper insights, drive informed decision-making, and ensure the health and longevity of their assets. It’s not just about collecting data anymore; it’s about making the data work smarter and more efficiently, all within a centralized portal.
Outsourcing data analysis offers several distinct advantages:
- Predictive Analytics: Predictive analytics in the context of drone inspections refers to using advanced data analysis techniques to anticipate potential issues or failures based on patterns identified from collected data. Drones with various sensors and cameras can capture detailed, high-resolution images of infrastructure, equipment, or environments. By analyzing this data, stakeholders can predict where and when maintenance or interventions might be needed. The predictive insights drawn from this analysis enhance safety and efficiency and lead to cost savings by addressing potential problems before they escalate.
- Strategic Vegetation Encroachment Management: Vegetation encroachment on powerlines refers to the growth or spread of trees, shrubs, and other plants in close proximity to electrical transmission and distribution lines, posing risks like fires, outages, and damage to the infrastructure. Uncontrolled vegetation can directly contact the powerlines, leading to electrical arcs and potential power disruptions. Drone inspections offer an efficient and safe means to monitor and assess the extent of this encroachment. Equipped with high-resolution cameras and sensors, drones can cover vast stretches of powerlines faster than ground-based inspections, providing detailed imagery that helps utilities identify and prioritize areas where vegetation management is most urgently needed.
- Expertise on Demand: Outsourcing provides access to experts in data analytics, ensuring high-quality insights without the overhead costs of hiring full-time specialists.
- Scalability: Whether dealing with data from a few drones or a fleet, outsourced data centers can scale their resources to meet your needs. This flexibility means you only pay for what you use.
- Advanced Tools and Techniques: Outsourced data centers often have the latest tools and technologies for data processing. This ensures accurate insights and means companies can save time investing in updating their in-house tools.
- Cybersecurity: Data, especially when related to critical infrastructure like T&D, is sensitive. Reputable outsourced data analysis providers prioritize cybersecurity, ensuring that your data remains protected from breaches.
The Technology Behind Drones
Drones often use various advanced technologies to enhance their efficacy when inspecting power lines, transmission towers, and substations.
Here are some of the specific technologies that augment the advantages of drone inspections in this field:
- High-Resolution Cameras: Beyond capturing clear visuals, these cameras can detect subtle changes in infrastructure color, texture, or material, which may indicate wear, corrosion, or other types of damage.
- Thermal Imaging: Through infrared sensors, thermal cameras highlight temperature anomalies. A higher-than-normal temperature could suggest overloaded equipment, while cooler spots might reveal a malfunctioning component, aiding in preventive maintenance.
- LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging): By emitting rapid laser pulses and measuring their reflections, LiDAR constructs detailed topographical maps. Because these laser pulses can penetrate through vegetation and tree canopies, it can identify deformities or inconsistencies in structures and terrain that might be hidden from the naked eye.
- Zoom Cameras: These cameras can magnify specific areas of interest, allowing for detailed scrutiny of connectors, insulators, and other components, even from a considerable distance.
- Corona Ultraviolet (UV) Sensors: Beyond detecting corona discharges, UV sensors highlight points of electrical leakage. Although invisible to the human eye, these discharges can erode equipment and lead to failures.
- Gas Sniffers: By identifying specific chemical markers in the air, gas sniffers can trace even minute gas leaks, safeguarding against potential fires, explosions, or toxic exposure.
- Magnetometers: By quantifying magnetic fields, they can identify variations in equipment operation. For instance, a misaligned transformer core might produce a unique magnetic signature.
- GIS (Geographic Information System) Integration: Beyond spatial analysis, GIS tools can correlate drone data with other layers of information, like historical maintenance records or environmental data, providing a holistic view of the infrastructure’s health.
- Real-time Data Transmission: Immediate data relay not only speeds up analysis but also allows operators to redirect drones on the fly if a potential issue or area of interest is spotted, maximizing the efficiency of each flight. Real-time data transmission is HUGE. Using Wi-Fi, 4G/5G, or satellite communication, drones can send data instantaneously to command centers or cloud platforms for analysis in nearly real-time for critical inspections.
- Automated Flight Paths: Pre-defined routes ensure that inspections cover every part of the infrastructure consistently, eliminating human error and ensuring every area is inspected. These automated flight paths can be duplicated repeatedly to ensure nearly identical aerial intelligence is captured for every flight.
By employing these technologies with drones, inspections of power lines, transmission towers, and substations are more comprehensive and packed with layers of nuanced data that traditional methods could scarcely achieve.
T&D Asset Breakdown and the Ecosystem Supporting Them
T&D Assets
- Transmission Lines (conductors) and Towers (typically metal): These are the high-voltage lines and structures you see stretching across long distances. They’re designed to transmit electricity from power plants to substations closer to consumption points.
- Distribution Lines and Poles (typically wood): Operating at lower voltages than transmission lines, distribution lines transport electricity from local substations to businesses, homes, and other consumers.
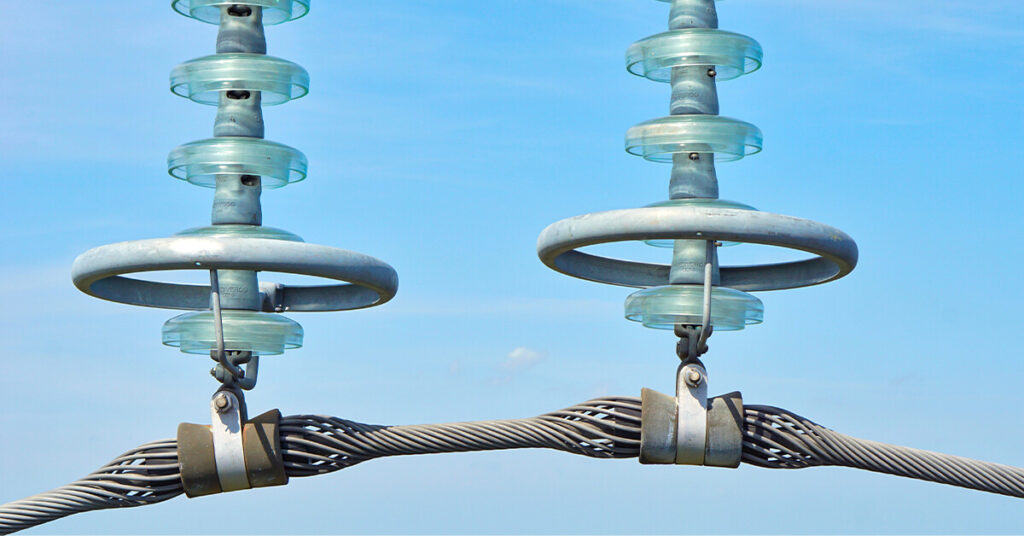
- Insulator Strings: Insulator strings, made of materials like porcelain or polymers, are essential in transmission and distribution systems. They electrically separate live conductors from grounded towers or poles, preventing electrical discharges and short circuits. Additionally, they provide mechanical support to the conductors and are designed to resist environmental challenges, ensuring safe and efficient power transmission.
- Substations: These facilities contain equipment for switching, transforming, and regulating electrical voltage. They serve as nodes where electricity’s voltage is converted from high to low (or vice versa) and where it can be routed in different directions.
- Capacitors and Reactors: These are used to manage and correct the power factor in the system, ensuring efficient power transmission.
- Switchgear and Circuit Breakers: These components control and protect the electrical circuits by interrupting the flow of electricity when faults are detected.
- Transformers: Devices that change the voltage levels of electricity. They can either step up the voltage (for transmission) or down the voltage (for distribution to end-users).
- Meters: Devices that measure and record the amount of electricity end-users consume.
- Protective Devices: This category includes relays, fuses, and other equipment that detects and responds to faults, ensuring system safety and reliability.
Ecosystem Behind T&D
- Generation: This is where the journey starts. Power plants—whether coal, nuclear, hydroelectric, wind, solar, or other types—generate electricity, which is then fed into the transmission system.
- Control Centers: These are the nerve centers of the T&D system. They monitor and control the flow of electricity throughout the grid, ensuring that supply matches demand and that the system remains stable and efficient.
- Maintenance and Inspection: Regular checks and upkeep of T&D assets, including drone inspections, vegetation management around power lines, and equipment repairs or replacements.
- Regulation and Policy: Governing bodies set standards and policies to ensure the safe, reliable, and sustainable operation of the T&D system.
- Consumer Interaction: This encompasses billing systems, customer service, and demand-response initiatives where consumers can adjust their electricity usage in response to grid conditions.
- Research and Development: Constant innovations aimed at improving the efficiency, reliability, and sustainability of the T&D system, from innovative grid technologies to new materials for power lines.
- Environmental Considerations: Assessing and mitigating the environmental impact of T&D operations, such as land use issues related to power line rights-of-way or potential effects on wildlife.
The T&D ecosystem is a complex web of interconnected components, operations, and stakeholders, working harmoniously to ensure electricity is generated, transmitted, distributed, and consumed efficiently and safely.